EDI vs API – Understanding Definitions, Differences, and Benefits of EDI API Integration

Which is more promising: API or EDI?
You may have found yourself considering this question while searching for an API solution for EDI transactions. In today’s fast-paced supply chain environment, efficient B2B data exchange is essential, and EDI API software is leading the way.
In just a few decades, global data exchange in supply chains has increased a hundredfold, making delays and inaccuracies intolerable for a company’s growth. Effective data exchange relies on B2B integration APIs. Before you choose your integration software, it’s important to grasp the basics of EDI and API performance.
What is EDI?
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is a digital format for exchanging business documents, such as purchase orders and invoices. An EDI file contains crucial data organized in a standardized format, which is defined by industry standards like ANSI X12 and UN EDIFACT.
For instance, a purchase order EDI document includes the purchase order number, quantity ordered, products selected, and other relevant data points. Similarly, an Advance Shipment Notification (ASN) includes information regarding the shipment that is expected to arrive.
Before the advent of computers, these exchanges happened through paper documents and emails. However, for large-scale environments like retail, those methods are not scalable. This limitation led to the development of modern EDI solutions a few decades ago, which have now been further enhanced through EDI modernization with API technology.
What is an API?
APIs, or Application Programming Interfaces, enable software systems to interact with each other. This interaction typically occurs through a protocol known as HTTP, often utilizing REST API for Electronic Data Interchange (EDI). Essentially, a client system sends a request like a question to access specific information and the server system responds with the appropriate answer. This process allows two systems to exchange information seamlessly in today’s digital landscape, facilitating real-time data sharing.
For instance, this is how Facebook can access your current location. The app uses the API provided by your mobile operating system to retrieve this information, but only if you have granted the Facebook app permission to do so. Similarly, if you want to view your order history at Walmart, the company offers an API for supply chain integration that organizations can utilize for transactions.
Many industry leaders are shifting their operations to API-based EDI platforms because these systems can easily incorporate the latest technologies into their work environments. This signifies a move towards embracing EDI alternatives in 2025.
Technical differences between EDI and API
Let’s take a look a closer look at the technical differences between EDI and API:
| EDI | API | |
| Data container | File | HTTP request and HTTP response |
| Communication method | AS2, SFTP | HTTP, HTTPS |
| Data structure | ANSI X12, EDIFACT, VDA, or any other EDI standard commonly used | Designed by the API host. |
Benefits of using EDI vs Benefits of using API
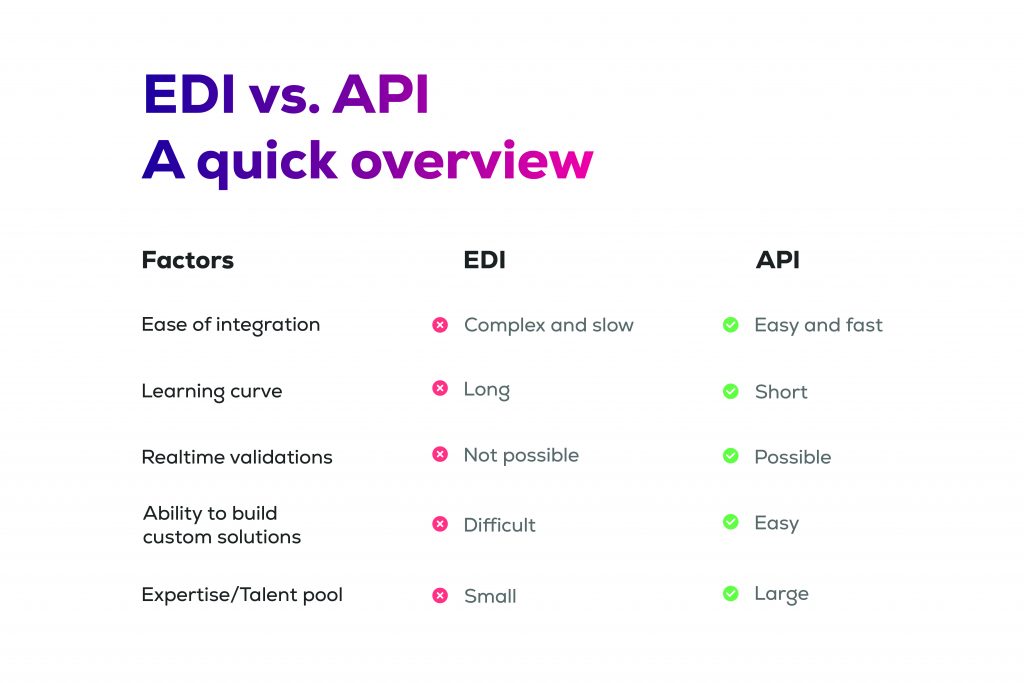
While both EDI and API serve their purpose for B2B integrations, there are significant differences that may be advantageous or disadvantageous depending on your existing B2B integration API infrastructure and the developer resources available within your organization, such as EDI developers versus API developers.
| EDI | API |
| Hard | Easy |
While you might get used to the structure of EDI standards if you are an EDI expert, for the average modern-day developer, hands down, API data structures such as JSON or XML are far easier to understand and deal with. Many businesses are now adopting an API for EDI transactions approach to simplify these integrations.
EDI data:
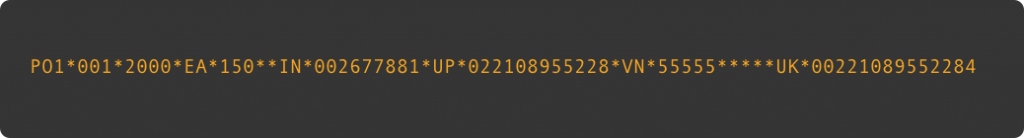
JSON data:
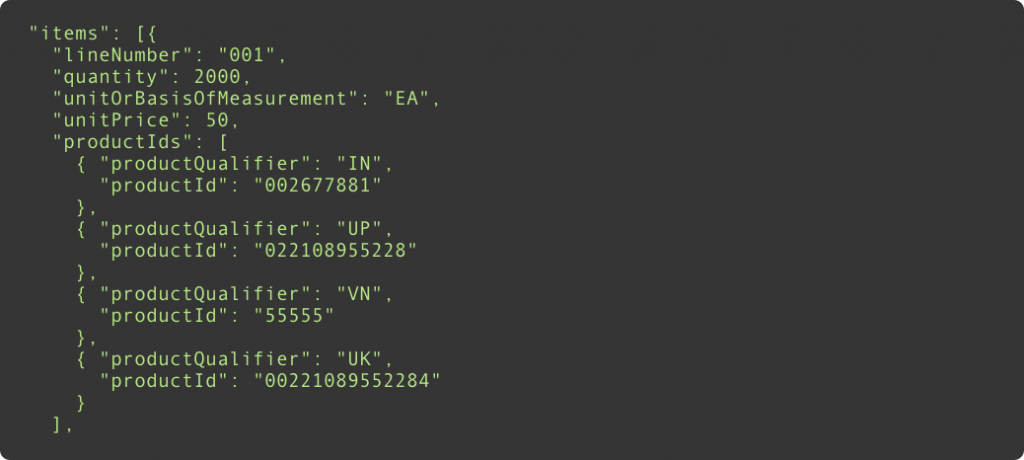
Ease of integration
| EDI | API |
| Hard | Easy |
The toolsets available for coding, testing, deploying, and maintaining B2B integration APIs in production are abundant. Cloud EDI API toolsets are much more advanced, mature, and user-friendly compared to traditional EDI software or platforms. Therefore, converting EDI to API in an ERP system has become a key focus for businesses.
Quality of data
| EDI | API |
| Prone to bad data | High-quality data with real-time validation |
Imagine applying for a visa and booking your tickets simultaneously, only to receive notification from the authorities days later, just before your journey, that your visa has been declined. This situation illustrates a major drawback of EDI today: the lack of real-time validation. EDI modernization through API addresses this challenge.
APIs enhance data accuracy and eliminate invalid data in real time. If you submit an invalid request, the API can validate your data against your trading partner’s requirements and reject it. This process helps eliminate bad data and chargebacks, showcasing the advantages of using APIs for EDI integration in retail.
Ease of automation
| EDI | API |
| Hard | Easy |
In today’s world, most modern systems, such as ERP, WMS, or financial software, interact through APIs. Integrating your systems with an API-based EDI platform ensures streamlined workflows. While it is possible to connect your EDI pipeline to other systems, doing so is complicated and often requires data transformations to convert EDI data into XML or JSON format, making end-to-end automation challenging.
Conversely, using APIs allows for seamless integration with external systems, enabling you to automate your entire workflow and facilitate real-time order processing more efficiently compared to EDI.
Availability of talent pool
| EDI developers | API developers |
| Small and rare | Commonly available |
According to Stack Overflow, the most readily available talent pool consists of API programmers. It is unrealistic to expect modern developers to learn traditional EDI methods unless there are compelling reasons to keep them engaged long-term. EDI developers are becoming increasingly scarce, and asking them to customize EDI processes beyond their regular integration tasks can create additional challenges. In contrast, there is a wealth of talent available for supply chain integration using APIs.
EDI vs API – Conclusion
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) remains prevalent mainly because many large organizations have made significant investments in it over the years. These companies cannot simply abandon EDI without recovering their investments, which is understandable. Therefore, they should consider enhancing their EDI infrastructure by integrating APIs through an EDI as API hybrid model. This can be achieved by building an API layer on top of the existing EDI framework. Data from APIs can be converted into EDI format and sent through the existing EDI infrastructure, addressing challenges associated with transitioning to EDI as API.
There is a growing trend of cloud EDI as API software designed for today’s developers. Organizations like Amazon and Walmart are increasingly utilizing both API and EDI. While they have maintained EDI channels for years, they are now establishing parallel API channels for integrations as well. This trend is expected to continue due to the benefits outlined earlier.
Although it may seem diplomatic to balance both approaches, it is clear that for the average modern developer, using REST APIs for EDI integrations is significantly easier for B2B transactions. Is EDI still relevant in the API era? While EDI continues to thrive, there are indications that API could eventually replace EDI in modern B2B integrations. The shift towards innovative EDI solutions suggests a future increasingly dominated by API-based EDI platforms.