
Transportation EDI – Support, Process, and Benefits
On April 18, 2023 by Shivam RawatOne of the most daunting processes in the transportation industry is reservation-based freight bidding. Being able to find the right carrier service every time while maintaining a resource management strategy is not easy, even with a Transport Management System (TMS), if it lacks automation in data exchange. In order to prevent communication loss from obstructing the busy workflow and ship orders at reasonably priced tenders, there is a need for EDI integration with the TMS of a transportation business.
In this article, we will discuss the support and process of EDI in the transportation industry, EDI documents in transportation, and some benefits of API for EDI integrations.
What is the EDI in Transportation?
In transportation, EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) is the data interchange process where trading parties share data using EDI standards specific to the transportation industry. Each EDI document serves its own business purpose, helping transportation businesses carry out various operations with computerized accuracy.
EDI integration with TMS is used by shippers, carriers, warehouses, 3PLs, brokers, and other parties, such as manufacturers and retailers. Let’s find out why EDI is important for your transportation business.
How Does EDI Support Transportation?
EDI helps a transportation business send, receive, and store information with minimal human involvement. It frees up the workforce that can then take on higher-tier responsibilities such as managing integrated systems or building healthy business relations with trading partners and customers.
EDIs can help you find the best carriers for your goods. Since the data exchange with various carriers happens at high speed, you can save time in finding a freight bid that fulfills your shipping requirements at reasonable prices.
The TMS workflow is such that it involves various parties in the supply chain to maintain a logical sequence and handle their individual operations effectively. If one link breaks due to miscommunication, it directly affects the business serving its customers. EDI optimizes and automates communication in the entire supply chain, ensuring the whereabouts of the order from the manufacturing facility to your customer’s doorstep.
The Process of Transportation EDI
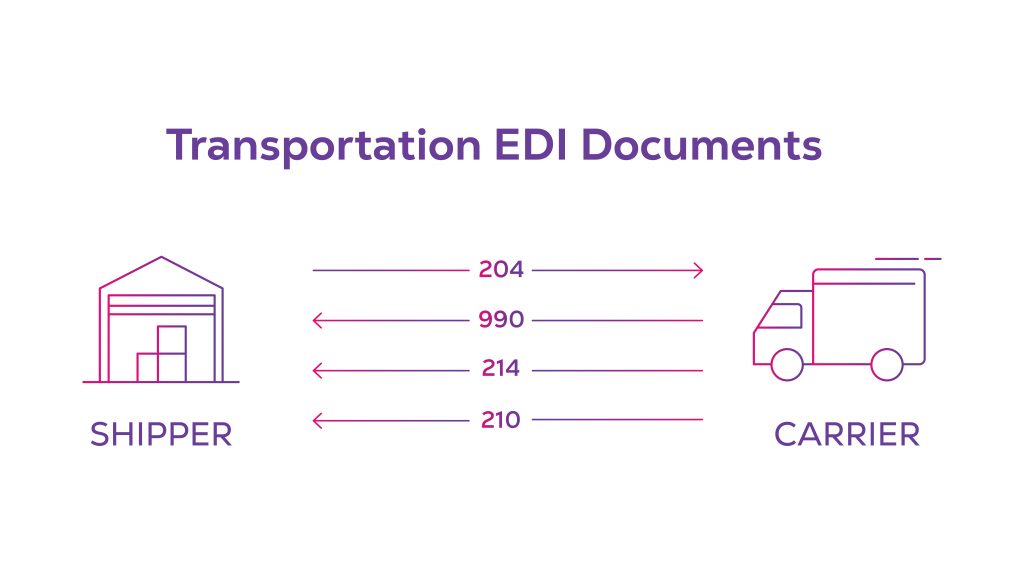
There are four steps in the process of transportation EDI
- When a shipper wants to tender a shipment order to a freight carrier, EDI 204 is sent to a list of carrier operators. It is managed by the TMS that the shipper uses. When sending EDI 204, the shipper shares a detailed document containing pick-up and delivery information about the order.
- A number of freight carriers receive tender requests from the shipper, and they decide whether they want to accept or reject the request. Irrespective of what they choose, all carriers send a response to EDI 204 of the shipper with their decision using EDI 990.
- Once a carrier accepts the tender and the shipper agrees with the carrier’s terms (such as pricing and delivery date estimations), the carrier picks up the order on the assigned date. Simultaneously, the carrier sends an order status to the shipper using EDI 214, which acts as proof of taking the order from the shipper.
- In the final step of the transportation process, the carrier sends an invoice for the picked order to the shipper. It contains all expense details that accumulate during the transportation period. This billing or expense report is sent to the shipper via EDI 210.
EDI Documents Used in Transportation
Here are the four commonly used EDI documents in transportation.
EDI 204 – Motor carrier load tender
EDI 204 is sent by shippers and traders to tender a shipment to motor carriers. It contains instructions to handle goods, the expected shipment schedule, equipment requirements, and the commodities related to a load.
EDI 990 – Response to a load tender
EDI 990 is sent as a response to EDI 204. It is used when a motor carrier accepts or rejects a tender from a shipper. It contains information about the item from EDI 204, a note of acceptance/rejection of the shipment, and any additional conditions or reasons stated by the motor carrier.
EDI 214 – Transportation carrier shipment status message
EDI 214 is used by transportation carriers to update shipment statuses to shippers or other trading partners. It contains shipping tracking details like time, date, location, item identification number, current route, and conveyance.
EDI 210 – Motor carrier freight details and invoice
EDI 210 is used when a motor carrier taking an order must send an invoice to a shipper along with the details of individual service charges. It contains details such as the date, order number, shipment size, mode, route, the amount due, and payment terms.
Benefits of API-based EDI in Transportation
The transportation industry is spread across the land and sea, working 24×7 so we can receive our goods on time, no matter which corner of the world we order from. Managing customers and keeping up with their demands can heat the workflow to levels where manually handling everything becomes nearly impossible. That is why a transportation business requires a modern solution like API that can automate processes as or when required. Let’s take a look at the benefits of API-based EDI in transportation.
Better accessibility
Modern APIs for EDI are accessible from anywhere as they provide cloud storage to all your supply chain data, whereas earlier methods would want you to reach your hardware to access data.
Realtime visibility
You can achieve real-time visibility over your supply chain data exchange using APIs. Any discrepancies, such as delays, lost items, returns, etc., can be handled or prevented when you can immediately send, receive, or retrieve EDI documents.
Resource savings
Businesses that are still relying on manual communication or traditional EDI processes pay for operations with time and money. API can automate maximum TMS EDI integration, which minimizes labor and operational costs while ensuring a higher return on investment.
Conclusion
There are modern APIs for EDI integration that simplify EDI elements that earlier required extensive experience, making them apt for small transportation, shipping, carrier, and brokerage businesses. We have discussed the pros and cons of each type of EDI integration solution in a detailed decision-making guide to help you make the right choice for your business.
To learn about the pre-built EDI workflows for transportation in Zenbridge’s API for EDI or to use a free EDI test environment, schedule a demo by clicking here.

Leave a Reply